Introduction
The Tokyo Institute of Technology has created and maintains a collection of exercises on NLP called "NLP 100 Exercise".
In this article, I will find sample answers to "Chapter 4: POS tagging".
Environment settings
The zip archive alice.zip contains the novel, Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland (written by Lewis Carroll) distributed on Project Gutenberg, as a text file
alice.txt. Apply a part-of-speech (POS) tagger to the text file, and store the result in another file. Implement programs that read the POS tagging result and perform the jobs.For your convenience, the zip archive also includes
alice.txt.conll, the novel with part-of-speech labels predicted by Stanford CoreNLP. It may be a good idea to use matplotlib or Gnuplot for the problems 37, 38, and 39.
$ wget https://nlp100.github.io/data/alice.zip
$ unzip alice.zip
$ head -n 15 alice.txt.conll
1 ALICE ALICE NNP _ _ _
2 'S 's POS _ _ _
3 ADVENTURES ADVENTURES NNP _ _ _
4 IN in IN _ _ _
5 WONDERLAND WONDERLAND NNP _ _ _
1 Lewis Lewis NNP _ _ _
2 Carroll Carroll NNP _ _ _
1 THE the DT _ _ _
2 MILLENNIUM MILLENNIUM NNP _ _ _
3 FULCRUM FULCRUM NNP _ _ _
4 EDITION EDITION NNP _ _ _
5 3.0 3.0 CD _ _ _
30. Reading the result
Implement a program that reads the result of part-of-speech tagging. Here, represent a sentence as a list of mapping objects, each of which associates a surface form, lemma (base form), part-of-speech tag with the keys
text,lemma,pos. Use this representation in the rest of the problems.
sentences = []
morphs = []
with open('./alice.txt.conll', mode='r') as f:
for line in f:
if line != '\n':
fields = line.split('\t')
if fields[1] == '':
continue
else:
morph = {
'text': fields[1],
'lemma': fields[2],
'pos': fields[3],
}
morphs.append(morph)
else:
if len(morphs) > 0:
sentences.append(morphs)
morphs = []
from pprint import pprint
for morpheme in sentences[:3]:
pprint(morpheme)
[{'lemma': 'ALICE', 'pos': 'NNP', 'text': 'ALICE'},
{'lemma': "'s", 'pos': 'POS', 'text': "'S"},
{'lemma': 'ADVENTURES', 'pos': 'NNP', 'text': 'ADVENTURES'},
{'lemma': 'in', 'pos': 'IN', 'text': 'IN'},
{'lemma': 'WONDERLAND', 'pos': 'NNP', 'text': 'WONDERLAND'}]
[{'lemma': 'Lewis', 'pos': 'NNP', 'text': 'Lewis'},
{'lemma': 'Carroll', 'pos': 'NNP', 'text': 'Carroll'}]
[{'lemma': 'the', 'pos': 'DT', 'text': 'THE'},
{'lemma': 'MILLENNIUM', 'pos': 'NNP', 'text': 'MILLENNIUM'},
{'lemma': 'FULCRUM', 'pos': 'NNP', 'text': 'FULCRUM'},
{'lemma': 'EDITION', 'pos': 'NNP', 'text': 'EDITION'},
{'lemma': '3.0', 'pos': 'CD', 'text': '3.0'}]
[{'lemma': 'chapter', 'pos': 'NN', 'text': 'CHAPTER'},
{'lemma': 'i.', 'pos': 'NN', 'text': 'I.'},
{'lemma': 'down', 'pos': 'IN', 'text': 'Down'},
{'lemma': 'the', 'pos': 'DT', 'text': 'the'},
{'lemma': 'Rabbit-Hole', 'pos': 'NNP', 'text': 'Rabbit-Hole'}]
31. Verbs
Extract surface forms of all verbs appearing in the text.
result = set()
for sentence in sentences:
for morph in sentence:
if morph['pos'].startswith('VB'):
result.add(morph['text'])
print(list(result)[:10])
['flashed', 'takes', 'died', 'play', 'produced', 'favoured', 'exclaimed', 'is', 'bring', 'folded']
32. Base forms of verbs
Extract lemmas of all verbs appearing in the text.
result = set()
for sentence in sentences:
for morph in sentence:
if morph['pos'].startswith('VB'):
result.add(morph['lemma'])
print(list(result)[:10])
['play', 'jog', 'bring', 'receive', 'settle', 'drop', 'continue', 'nurse', 'last', 'cross-examine']
33. A of B
Extract noun phrases in the form of “A of B”, where A and B are nouns.
result = set()
for sentence in sentences:
for i in range(1, len(sentence) - 1):
if sentence[i - 1]['pos'].startswith('NN') and sentence[i]['text'] == 'of' and sentence[i + 1]['pos'].startswith('NN'):
result.add(sentence[i - 1]['text'] + ' ' + sentence[i]['text'] + ' ' + sentence[i + 1]['text'])
print(list(result)[:5])
['Adventures of hers', 'way of nursing', 'state of mind', 'clapping of hands', 'piece of rudeness']
34. A B
Extract the longest noun phrase consisting of consecutive nouns.
result = set()
for sentence in sentences:
nouns = ''
count = 0
for morph in sentence:
if morph['pos'].startswith('NN'):
if count == 0:
nouns = morph['text']
else:
nouns = ' '.join([nouns, morph['text']])
count += 1
elif count >= 2:
result.add(nouns)
nouns = ''
count = 0
else:
nouns = ''
count = 0
if count >= 2:
result.add(nouns)
pprint(list(result)[:10])
['summer days',
'Ou est ma chatte',
'CHAPTER I.',
'feather flock',
'head downwards',
'glass box',
'ITS WAISTCOAT-POCKET',
'Miss Alice',
'Mock Turtle',
'garden door']
35. Frequency of words
Obtain the list of words and frequencies of their occurrences sorted by descending order of frequency.
from collections import defaultdict
result = defaultdict(int)
for sentence in sentences:
for morph in sentence:
if morph['pos'] not in [',', '.', ':', '$', '#', '"', "''", '``', '-LRB-', '-RRB-']:
result[morph['lemma']] += 1
result = sorted(result.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for res in result[:10]:
print(res)
('the', 1639)
('be', 1076)
('and', 866)
('she', 794)
('to', 725)
('a', 688)
('I', 604)
('it', 594)
('say', 532)
('of', 511)
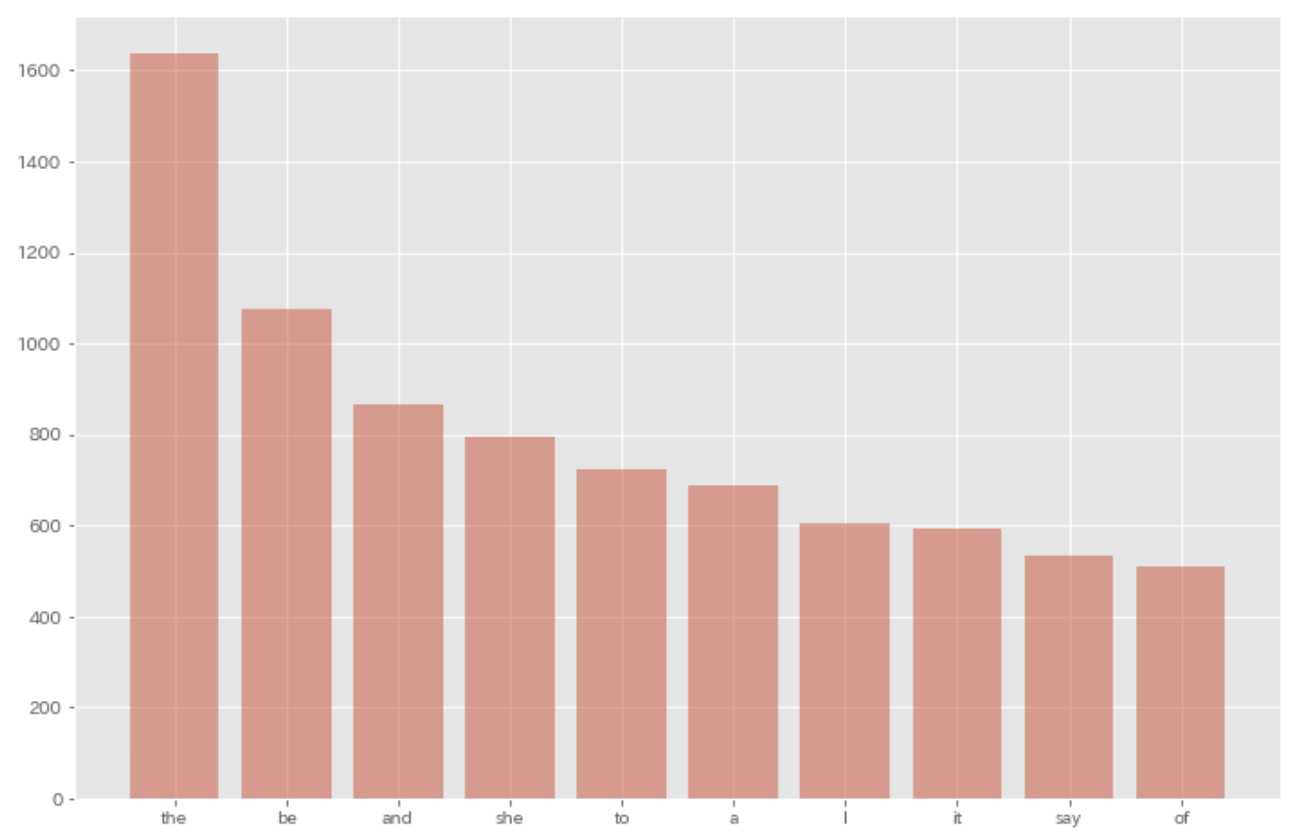
36. Top-ten frequent words
Visualize the top-ten frequent words and their frequencies with a chart (e.g., bar chart).
$ pip install japanize_matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use('ggplot')
result = defaultdict(int)
for sentence in sentences:
for morph in sentence:
if morph['pos'] not in [',', '.', ':', '$', '#', '"', "''", '``', '-LRB-', '-RRB-']:
result[morph['lemma']] += 1
result = sorted(result.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.bar([res[0] for res in result[0:10]], [res[1] for res in result[0:10]], alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
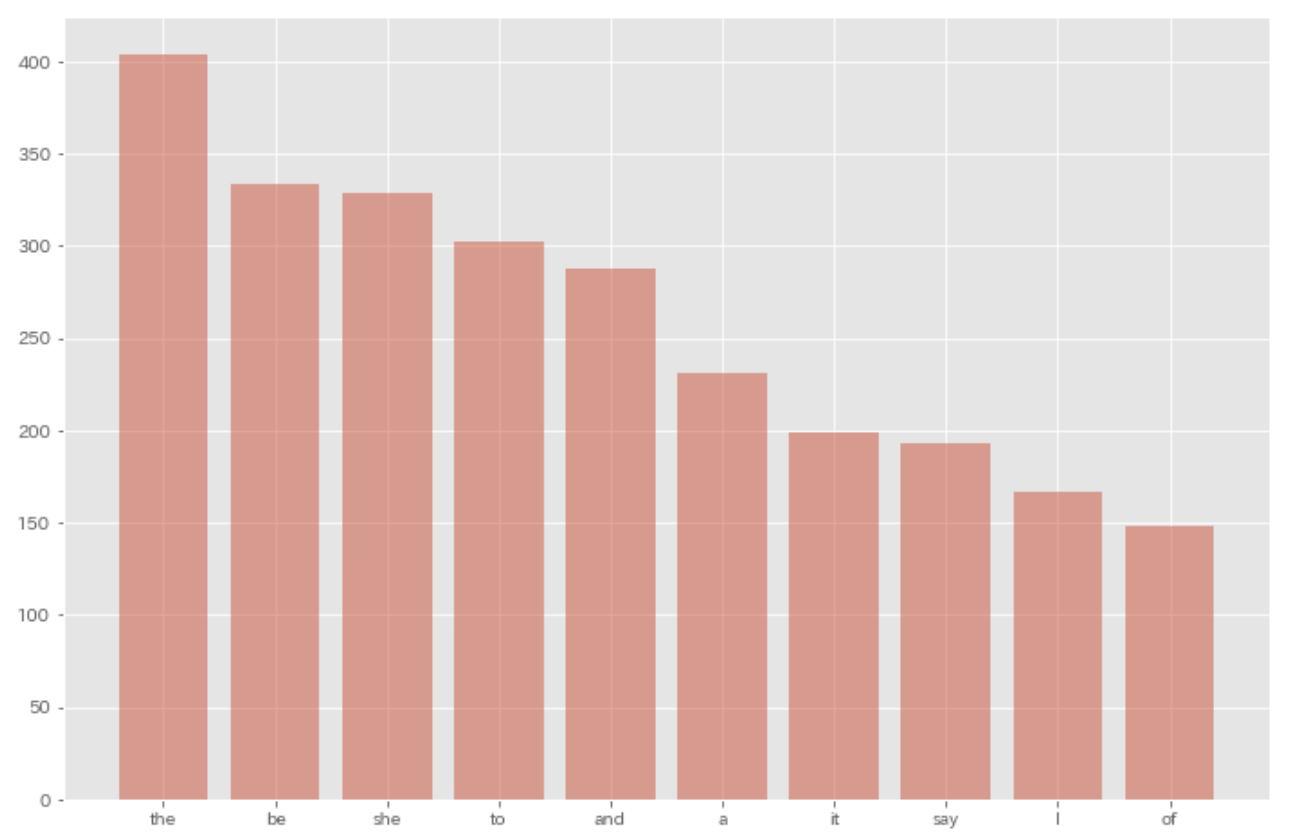
37. Top-ten words co-occurring with ‘Alice’
Extract the list of words that co-occur with the word “Alice”. Visualize with a chart (e.g., bar chart) the top-ten words co-occurring with the word “Alice” and their frequencies.
result = defaultdict(int)
for sentence in sentences:
if 'Alice' in [morph['text'] for morph in sentence]:
for morph in sentence:
if morph['pos'] not in [',', '.', ':', '$', '#', '"', "''", '``', '-LRB-', '-RRB-'] and morph['text'] != 'Alice':
result[morph['lemma']] += 1
result = sorted(result.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.bar([res[0] for res in result[0:10]], [res[1] for res in result[0:10]], alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
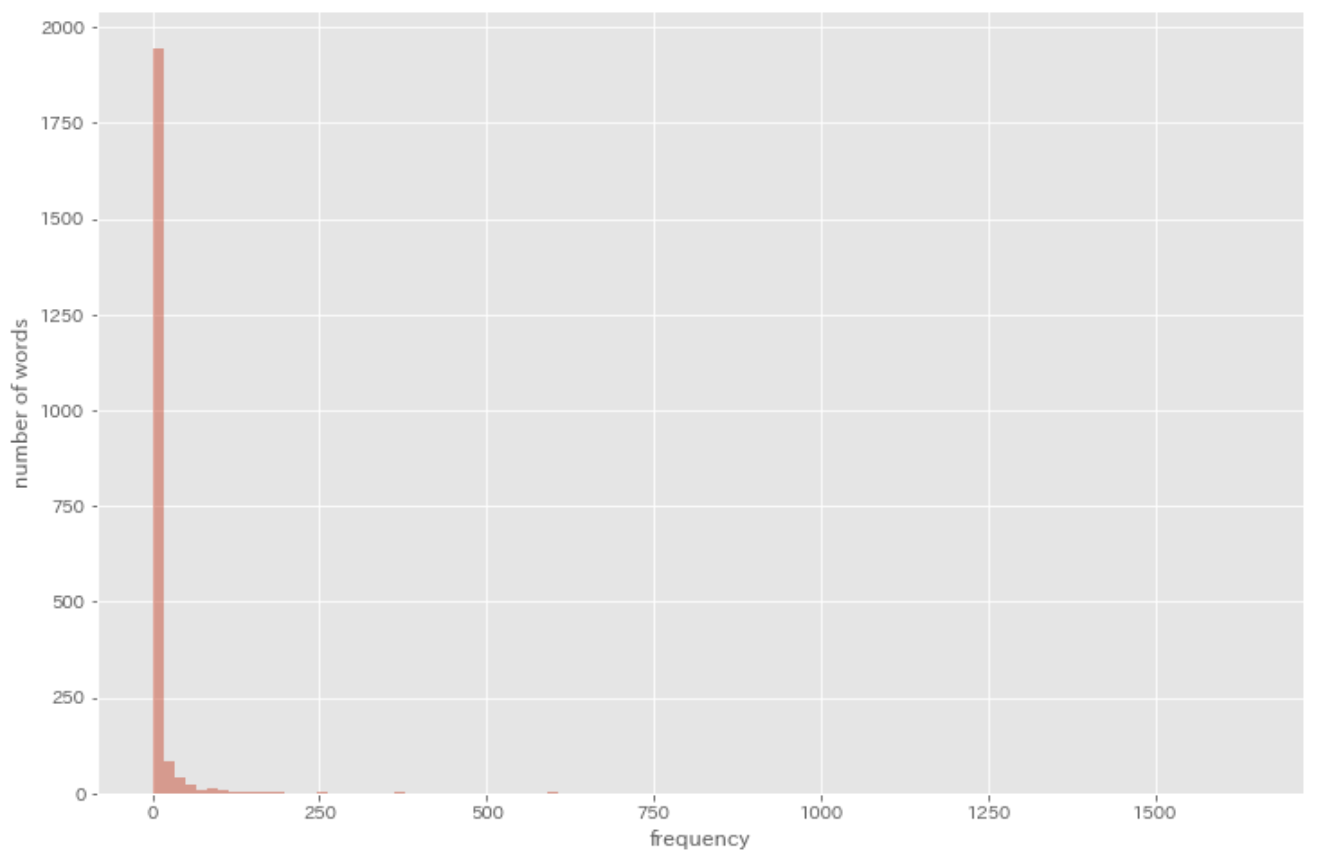
38. Histogram
Draw a histogram of word frequency (x-axis is a scalar range representing a frequency ranging from 1 to the largest frequency of a given word in the entire corpus, and the y-axis is the count of unique words that fall into the count of the x value).
result = defaultdict(int)
for sentence in sentences:
for morph in sentence:
if morph['pos'] not in [',', '.', ':', '$', '#', '"', "''", '``', '-LRB-', '-RRB-']:
result[morph['lemma']] += 1
result = result.values()
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.hist(result, bins=100, alpha=0.5)
plt.xlabel('frequency')
plt.ylabel('number of words')
plt.show()
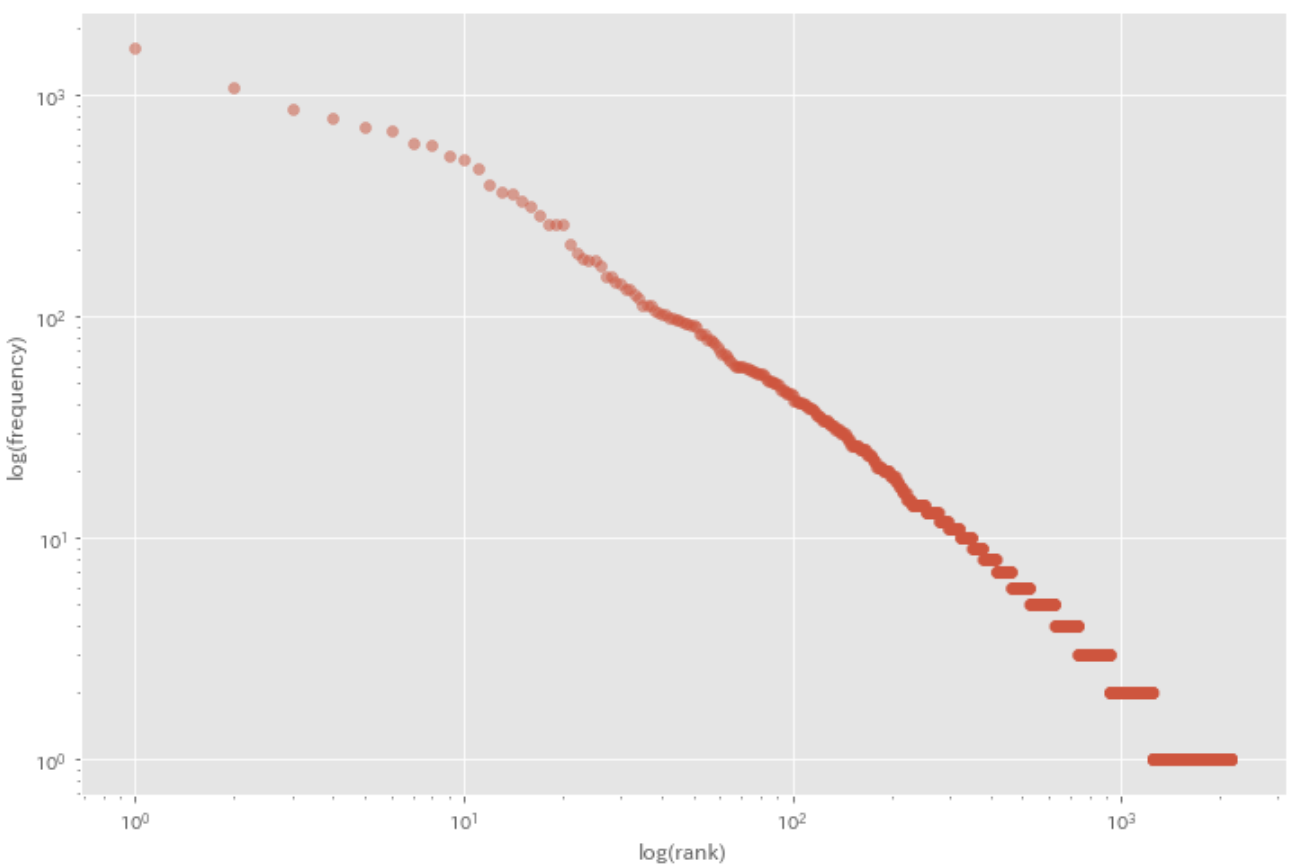
39. Zipf’s law
Plot a log-log graph with the x-axis being rank order and the y-axis being frequency.
result = defaultdict(int)
for sentence in sentences:
for morph in sentence:
if morph['pos'] not in [',', '.', ':', '$', '#', '"', "''", '``', '-LRB-', '-RRB-']:
result[morph['lemma']] += 1
result = sorted(result.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
ranks = [res + 1 for res in range(len(result))]
values = [res[1] for res in result]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.scatter(ranks, values, alpha=0.5)
plt.xscale('log')
plt.yscale('log')
plt.xlabel('log(rank)')
plt.ylabel('log(frequency)')
plt.show()
References