Model delivery Patterns
Container technology has made it common to run servers using container images of servers. However, the management and versioning of server images and inference model files is an important issue to consider.
There are two main ways to embed models in a server and run it as an inference server.
- Model-in-image pattern (a model is contained in an image)
- Model-load pattern (a model is loaded from server)
Model-in-image pattern
In the Model-in-image pattern, the model file is included in the image of the reasoner and built. By including the model in the image, it is possible to generate a reasoner dedicated to that model.
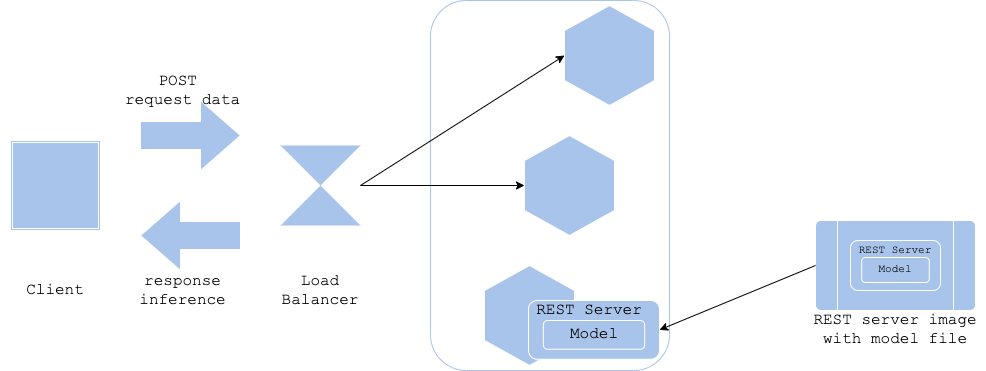
- Pros
- Keep server image and model file versions the same
- Cons
- Need to define pipeline from model training to server image building
- Increased inference server image size and longer time to get images loaded and running
- Use cases
- When you want to match the server image and inference model versions
Model-load pattern
In the Model-load pattern, the inference server is started, then the model files are loaded, and the inference server is put into production. The server image and inference model files are managed separately.
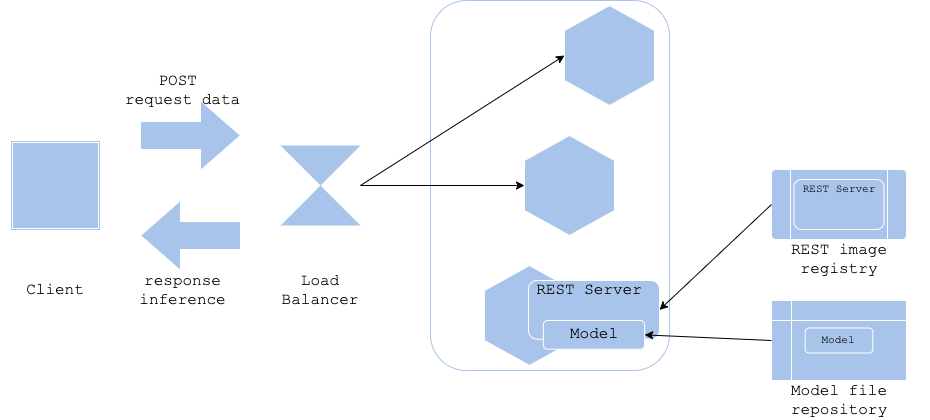
- Pros
- Can separate server image versions from model file versions
- Improved server image applicability
- Server images will be lightweight
- Cons
- Server deployment and model file loading are done in sequence, so it may take longer to start the inference server
- Requires versioning of server image and model files
- Use cases
- When the model file version is updated more frequently than the server image version
- When running multiple types of inference models on the same server image
References
AlloyDB
Amazon Cognito
Amazon EC2
Amazon ECS
Amazon QuickSight
Amazon RDS
Amazon Redshift
Amazon S3
API
Autonomous Vehicle
AWS
AWS API Gateway
AWS Chalice
AWS Control Tower
AWS IAM
AWS Lambda
AWS VPC
BERT
BigQuery
Causal Inference
ChatGPT
Chrome Extension
CircleCI
Classification
Cloud Functions
Cloud IAM
Cloud Run
Cloud Storage
Clustering
CSS
Data Engineering
Data Modeling
Database
dbt
Decision Tree
Deep Learning
Descriptive Statistics
Differential Equation
Dimensionality Reduction
Discrete Choice Model
Docker
Economics
FastAPI
Firebase
GIS
git
GitHub
GitHub Actions
Google
Google Cloud
Google Search Console
Hugging Face
Hypothesis Testing
Inferential Statistics
Interval Estimation
JavaScript
Jinja
Kedro
Kubernetes
LightGBM
Linux
LLM
Mac
Machine Learning
Macroeconomics
Marketing
Mathematical Model
Meltano
MLflow
MLOps
MySQL
NextJS
NLP
Nodejs
NoSQL
ONNX
OpenAI
Optimization Problem
Optuna
Pandas
Pinecone
PostGIS
PostgreSQL
Probability Distribution
Product
Project
Psychology
Python
PyTorch
QGIS
R
ReactJS
Regression
Rideshare
SEO
Singer
sklearn
Slack
Snowflake
Software Development
SQL
Statistical Model
Statistics
Streamlit
Tabular
Tailwind CSS
TensorFlow
Terraform
Transportation
TypeScript
Urban Planning
Vector Database
Vertex AI
VSCode
XGBoost