What is a Man-in-the-Middle Attack
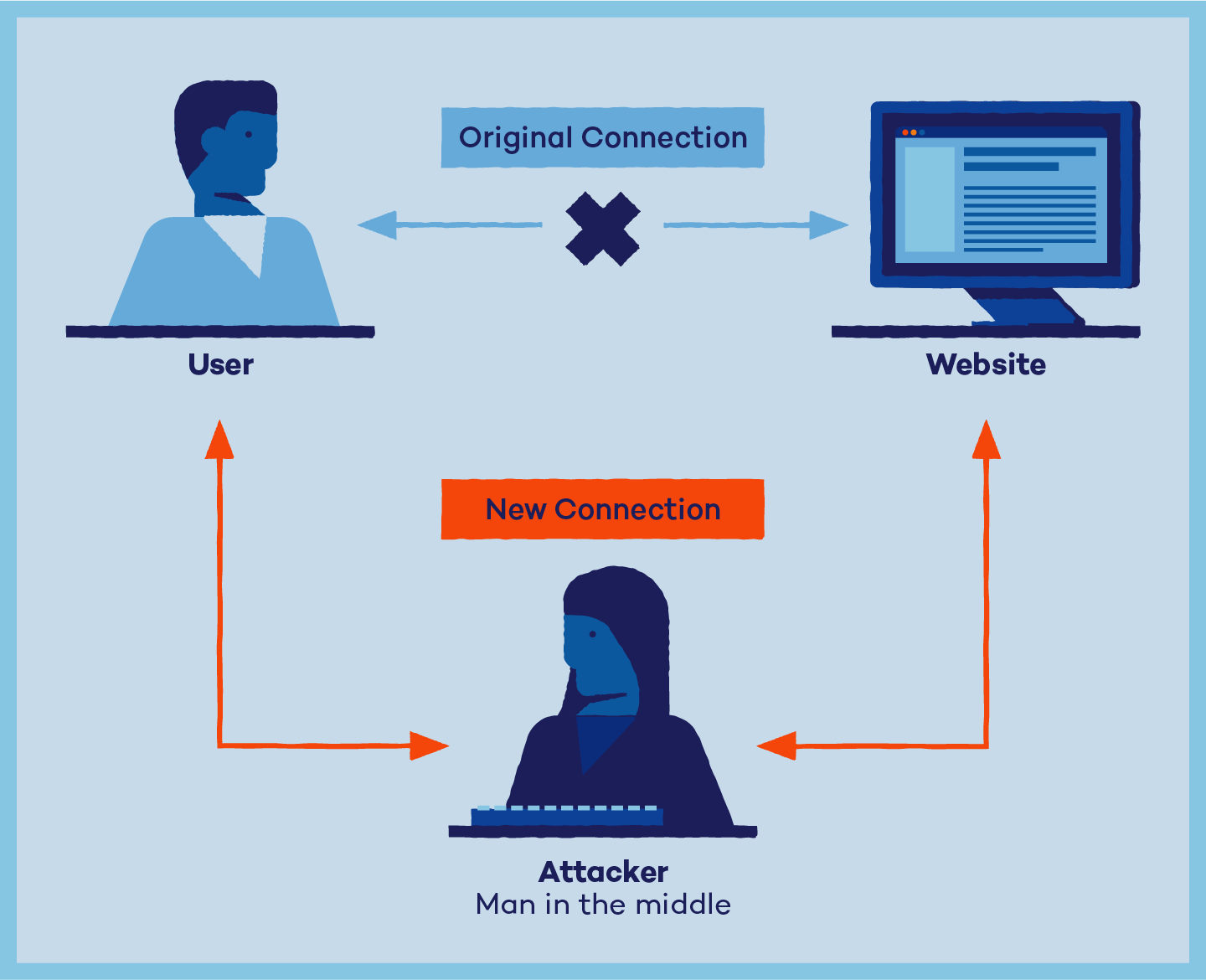
In the realm of cybersecurity, a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack is a malicious act where an attacker intercepts and potentially alters the communication between two parties without their knowledge. This attack takes advantage of the trust established between the communicating entities, inserting themselves as a covert intermediary. Essentially, the attacker positions themselves in the middle of the communication flow, gaining access to sensitive information and manipulating it to their advantage.
What Is a Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack? Definition and Prevention
How Does a Man-in-the-Middle Attack Work
To comprehend the workings of a Man-in-the-Middle attack, it's important to understand the step-by-step process typically employed by attackers:
-
Network Interception
The attacker infiltrates the communication channel between the sender and the intended recipient. This can be achieved through various means, such as compromising routers, gaining control over a Wi-Fi network, or exploiting vulnerabilities in network protocols. -
Session Hijacking
Once the attacker has successfully intercepted the network traffic, they proceed to hijack the session between the two parties. This involves assuming control over the communication session, effectively bypassing any security mechanisms in place. -
Data Manipulation
With control over the session, the attacker can now manipulate the data exchanged between the two parties. They may modify the content of messages, inject malicious code, or even replace legitimate files with malicious counterparts. -
Covert Observation
In some instances, the attacker may choose not to modify the communication directly but instead silently observe the exchanged information for later exploitation. This allows them to gather sensitive data, such as login credentials or financial details, without alerting the victims.
Types of Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Man-in-the-Middle attacks come in various forms, each targeting different aspects of the communication process. Here are some common types of MitM attacks:
-
SSL Stripping
This attack targets the secure communication protocol, SSL (Secure Sockets Layer), by downgrading the connection to an unencrypted format. By intercepting and modifying the initial connection request, the attacker can force the parties to communicate using an insecure channel, making it easier to extract sensitive information. -
DNS Spoofing
Domain Name System (DNS) spoofing involves tampering with the DNS resolution process. By redirecting the victim's requests to a malicious server controlled by the attacker, they can intercept and manipulate the communication before forwarding it to the intended destination. -
Wi-Fi Network Exploitation
Attackers can take advantage of unsecured or poorly configured Wi-Fi networks to launch MitM attacks. By creating a rogue access point or eavesdropping on the network traffic, they can intercept sensitive information transmitted over the Wi-Fi network. -
Email Hijacking
In this type of attack, the attacker gains control over the victim's email account, allowing them to intercept and modify incoming and outgoing messages. This can lead to unauthorized access to confidential information or the dissemination of malware.
It's important to note that these are just a few examples of Man-in-the-Middle attacks, and attackers are constantly developing new techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in communication systems.
Recognizing and Preventing Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Identifying Warning Signs
Recognizing the warning signs of a potential Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack is essential in mitigating the risks associated with such security breaches. While these attacks can be sophisticated, there are indicators that individuals and organizations should be aware of:
-
Unusual SSL Certificate Warnings
When accessing a website secured with SSL/TLS encryption, if you encounter unexpected SSL certificate warnings or errors, it could be an indication of a potential MitM attack. These warnings often occur when attackers attempt to use self-signed or forged certificates to intercept the secure connection. -
Unusual Network Behavior
If you notice sudden drops in network speed, unusual network traffic patterns, or frequent disconnections, it may signify the presence of a MitM attack. Pay attention to any suspicious network behavior and investigate further if necessary. -
Unexpected Certificate Authority (CA) Changes
If your device or web browser suddenly recognizes a different Certificate Authority as trusted or displays unrecognized CAs, it could indicate an attempt to manipulate the trust hierarchy and compromise secure connections. -
Unauthorized Certificate Issuance
If you discover that certificates have been issued without your knowledge or consent, it's a clear indication that someone may be intercepting and manipulating your communication. Regularly monitor and review your certificates for any unauthorized activity.
Implementing Strong Encryption Measures
Strong encryption is crucial in preventing and mitigating the risks of Man-in-the-Middle attacks. By implementing robust encryption measures, you can enhance the security of your communications and make it significantly harder for attackers to intercept and manipulate your data. Here are some essential encryption practices:
-
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Utilize the latest versions of SSL or TLS protocols for securing communication channels. It's important to keep these protocols up to date to avoid vulnerabilities associated with older versions. -
Digital Certificates
Acquire digital certificates from reputable Certificate Authorities (CAs) to ensure the authenticity and integrity of your communication. Regularly validate and monitor the certificates to detect any suspicious changes. -
Certificate Pinning
Implement certificate pinning, which involves associating a specific certificate or public key with a particular website or service. This practice adds an extra layer of security by reducing the risk of accepting unauthorized certificates during the SSL/TLS handshake.
Secure Communication Channels
To mitigate the risks of Man-in-the-Middle attacks, it's essential to establish secure communication channels. Consider the following measures:
-
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Utilize VPN services to create encrypted tunnels between your device and the destination server. VPNs provide secure and private communication, preventing attackers from intercepting data transmitted over public networks. -
End-to-End Encryption
Implement end-to-end encryption for sensitive communications, ensuring that only the intended recipients can decrypt and access the data. Services like Signal and WhatsApp employ end-to-end encryption, offering stronger protection against MitM attacks. -
Secure Email Communication
Use encrypted email services or implement Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) encryption to secure email communication. Encrypting the content of your emails ensures that even if intercepted, the information remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Regularly Updating and Patching Systems
Regularly updating and patching software and systems is crucial in preventing Man-in-the-Middle attacks. Software vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to launch MitM attacks. To mitigate these risks:
-
Operating System Updates
Install the latest security patches and updates for your operating system. These updates often include bug fixes and security enhancements that address vulnerabilities exploited by attackers. -
Application Updates
Keep all applications and software up to date, including web browsers, email clients, and other communication tools. Regularly check for updates and install them promptly to benefit from the latest security measures.