Kedro and Jupyter
Kedro can be developed in conjunction with Jupyter Notebook, Jupyter Lab, and IPython.
$ kedro jupyter notebook
$ kedro jupyter lab
$ kedro ipython
In [1]:
In [2]: exit()
Kedro variables
Kedro allows the following variables to be used within Jupyter Notebook.
catalogcontextpipelinessession
We will create a sample project for pandas-iris and check the above variables.
$ kedro new --starter=pandas-iris
$ cd iris
$ kedro jupyter notebook
Click New > Kedro (iris) to create a new notebook.
catalog
catalog allows you to search for a DataCatalog containing parameters.
In [1]: catalog.list()
[
'example_iris_data',
'parameters',
'params:train_fraction',
'params:random_state',
'params:target_column'
]
In [2]: catalog.load("example_iris_data")
INFO Loading data from 'example_iris_data' (CSVDataSet)...
sepal_length sepal_width petal_length petal_width species
0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa
2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa
3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa
... ... ... ... ... ...
145 6.7 3.0 5.2 2.3 virginica
146 6.3 2.5 5.0 1.9 virginica
147 6.5 3.0 5.2 2.0 virginica
148 6.2 3.4 5.4 2.3 virginica
149 5.9 3.0 5.1 1.8 virginica
150 rows × 5 columns
In [3]: catalog.load("parameters")
INFO Loading data from 'parameters' (MemoryDataSet)...
{'train_fraction': 0.8, 'random_state': 3, 'target_column': 'species'}
context
context provides access to kedro library components and project metadata.
In [4]: context.project_path
PosixPath('/Users/ryu/iris')
pipeline
Use pipeline to display the pipelines registered in your project.
In [5]: pipelines
{'__default__': Pipeline([
Node(split_data, ['example_iris_data', 'parameters'], ['X_train', 'X_test', 'y_train', 'y_test'], 'split'),
Node(make_predictions, ['X_train', 'X_test', 'y_train'], 'y_pred', 'make_predictions'),
Node(report_accuracy, ['y_pred', 'y_test'], None, 'report_accuracy')
])}
In [6]: pipelines["__default__"].all_outputs()
{'y_test', 'y_train', 'X_test', 'y_pred', 'X_train'}
session
The session can be used to execute the pipeline.
In [7]: session.run()
[01/15/23 09:24:05] INFO Kedro project iris session.py:340
[01/15/23 09:24:06] INFO Loading data from 'example_iris_data' (CSVDataSet)... data_catalog.py:343
INFO Loading data from 'parameters' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:343
INFO Running node: split: split_data([example_iris_data,parameters]) -> node.py:327
[X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test]
INFO Saving data to 'X_train' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:382
INFO Saving data to 'X_test' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:382
INFO Saving data to 'y_train' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:382
INFO Saving data to 'y_test' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:382
INFO Completed 1 out of 3 tasks sequential_runner.py:85
INFO Loading data from 'X_train' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:343
INFO Loading data from 'X_test' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:343
INFO Loading data from 'y_train' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:343
INFO Running node: make_predictions: make_predictions([X_train,X_test,y_train]) node.py:327
-> [y_pred]
INFO Saving data to 'y_pred' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:382
INFO Completed 2 out of 3 tasks sequential_runner.py:85
INFO Loading data from 'y_pred' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:343
INFO Loading data from 'y_test' (MemoryDataSet)... data_catalog.py:343
INFO Running node: report_accuracy: report_accuracy([y_pred,y_test]) -> None node.py:327
INFO Model has accuracy of 0.933 on test data. nodes.py:74
INFO Completed 3 out of 3 tasks sequential_runner.py:85
INFO Pipeline execution completed successfully. runner.py:90
%reload_kedro
You can reload Kedro variables by running %reload_kedro.
In [8]: %reload_kedro
[01/15/23 09:25:42] INFO Resolved project path as: /Users/ryu/iris. __init__.py:132
To set a different path, run '%reload_kedro <project_root>'
[01/15/23 09:25:43] INFO Kedro project Iris __init__.py:101
INFO Defined global variable 'context', 'session', 'catalog' and __init__.py:102
'pipelines'
INFO Registered line magic 'run_viz' __init__.py:108
Documentation for %reload_kedro can be found with the following command.
In [9]: %reload_kedro?
Docstring:
::
%reload_kedro [-e ENV] [--params PARAMS] [path]
The `%reload_kedro` IPython line magic. See
https://kedro.readthedocs.io/en/stable/tools_integration/ipython.html for more.
positional arguments:
path Path to the project root directory. If not given, use the
previously setproject root.
optional arguments:
-e ENV, --env ENV Kedro configuration environment name. Defaults to
`local`.
--params PARAMS Specify extra parameters that you want to pass to the
context initializer. Items must be separated by comma,
keys - by colon, example: param1:value1,param2:value2.
Each parameter is split by the first comma, so parameter
values are allowed to contain colons, parameter keys are
not. To pass a nested dictionary as parameter, separate
keys by '.', example: param_group.param1:value1.
File: ~/Program/MLOps/kedro/venv/lib/python3.8/site-packages/kedro/ipython/__init__.py
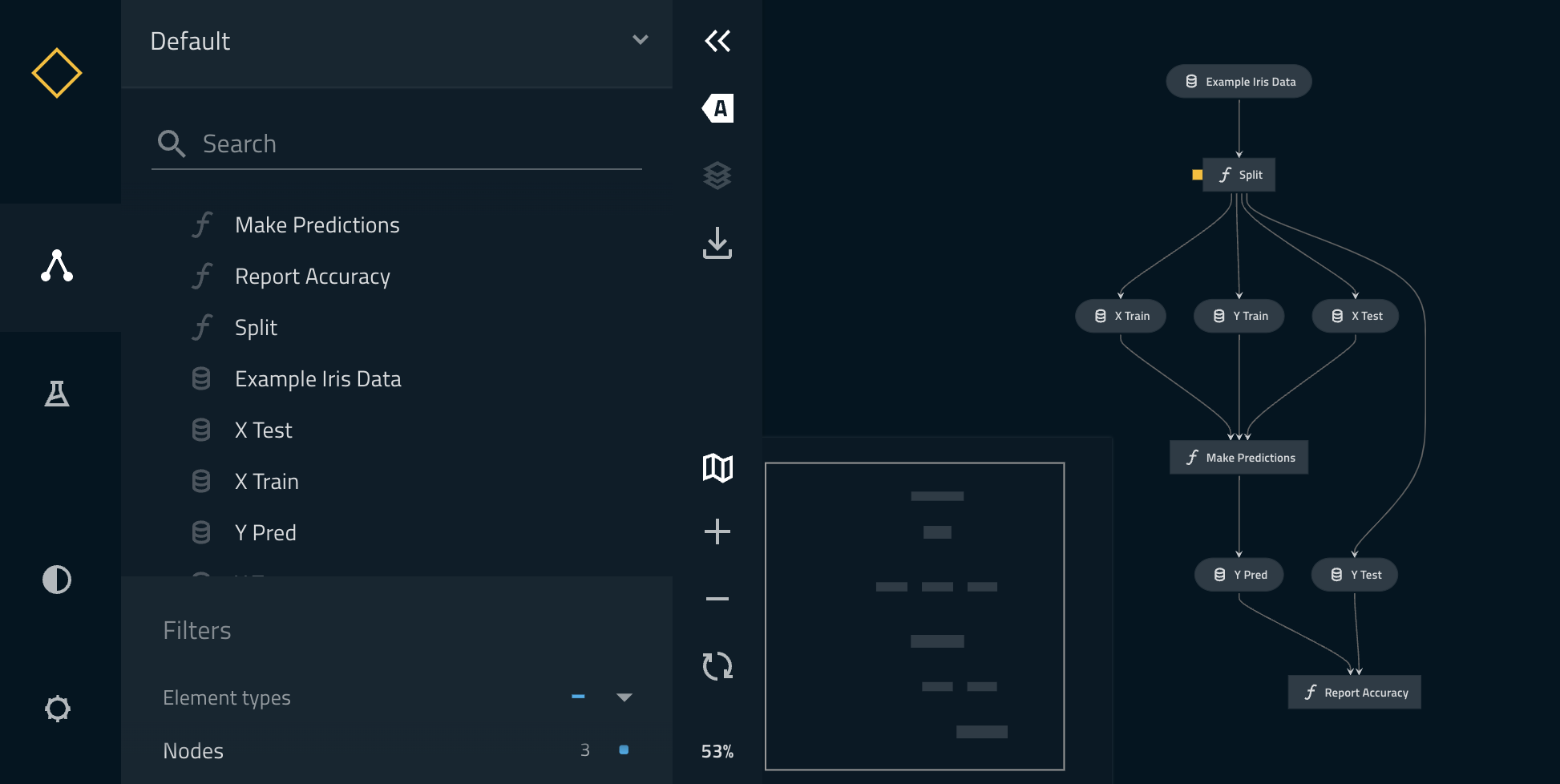
%run_viz
Run %run_viz to start Kedro-Viz.
In [10]: %run_viz
Convert Jupyter Notebook code to Node
Kedro allows you to copy code written in Jupyter Notebook to Node.
Suppose the following function is written in Jupyter Notebook.
def some_action():
print("This function came from `notebooks/my_notebook.ipynb`")
On Jupyter Notebook, click View > Cell Toolbar > Tags and add a node tag to the cell.
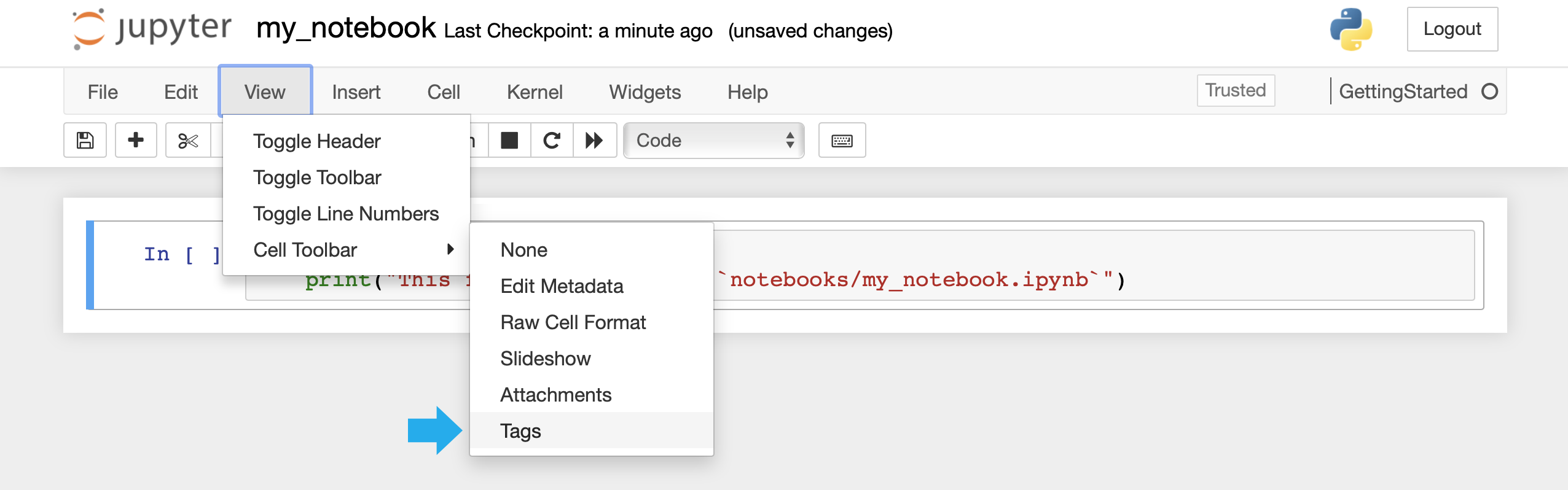
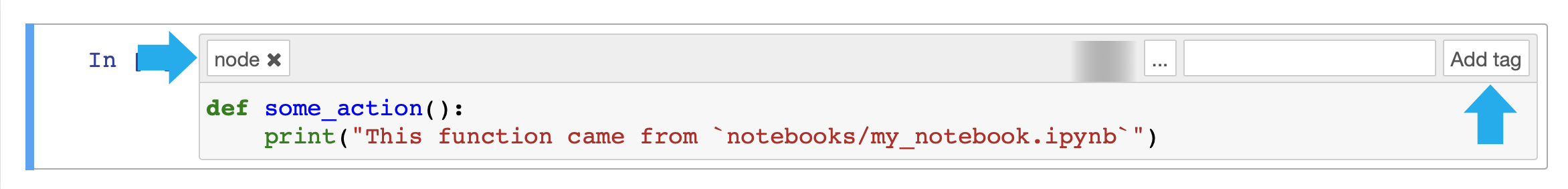
Save the Jupyter Notebook as my_notebook and move the files to the notebooks folder with the following command.
$ mv my_notebook.ipynb notebooks
Execute the following command.
$ kedro jupyter convert notebooks/my_notebook.ipynb
You can see that the function has been added to src/iris/nodes/my_notebook.py.
$ cat src/iris/nodes/my_notebook.py
def some_action():
print("This function came from `notebooks/my_notebook.ipynb`")
References