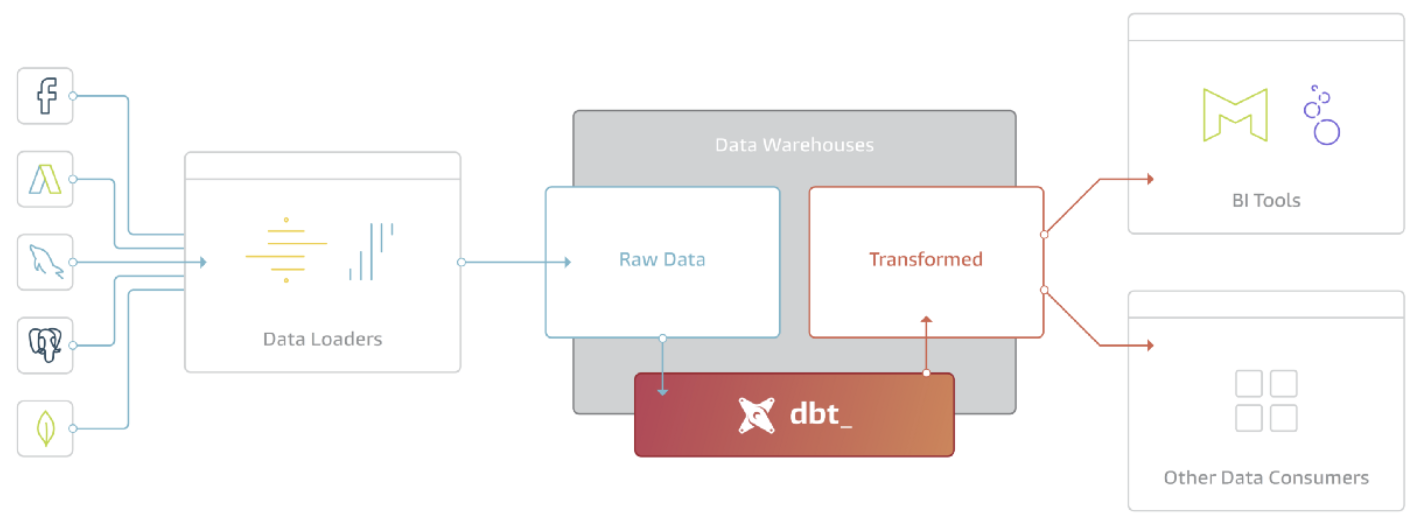
What is dbt
dbt is a tool that handles the T of ELT (Extract, Load, Transform). dbt performs only data transformation, and assumes that data has already been loaded onto a data warehouse (DWH) such as Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, or Snowflake. In other words, dbt is a tool that processes data stored in the DWH and writes the processed results back to the DWH.
dbt features
dbt has the following main features:
- SQL-based
dbt uses SQLSELECTto describe the data transformation process. - Advanced query processing by Jinja
dbt allows the use of Jinja, a lightweight template language, in SQL. This allows you to use control constructs such as if and for in your SQL, and to modularize your processing. - Documentation
dbt can figure out dependencies between models described in SQL and automatically generate documentation including schema and data lineage for each model. - Testing
dbt can check data for NULLs and referential integrity.
How to use dbt
dbt can be used in the following two ways:
- dbt Core (OSS)
- dbt Cloud (SaaS)
dbt Core is OSS and can be used free of charge. In contrast, dbt Cloud is SaaS and managed. dbt Cloud is free for a single user, but there is a fee for multiple users.
dbt Cloud has the following features in addition to dbt Core features:
- Development function
An IDE is provided to enable dbt-based development on a single screen. - Notifications
Connectivity to Slack and other social networking services. - Job management
A function to set up jobs and execute them on a scheduled basis is provided. - Environment variable management
Allows you to manage settings and variables for each environment. - Source code management
A git repository for managing dbt code is provided by default, so you can get started without GitHub, etc.
dbt Core Tutorial
Let's try to process BigQuery data using dbt Core: Suppose you have a dataset in BigQuery for a fictitious EC site named jaffle_shop. The dataset contains the following tables
raw_customersraw_ordersraw_payments
Create project
First, let us install dbt Core. dbt Core can be installed in the following 4 ways.
- Using Homebrew
- Using pip
- Using Docker image
- Using Github source code
This time, we will install dbt Core installed by pip.
$ mkdir dbt-projects && cd dbt-projects
$ python -m venv venv
$ source venv/bin/activate
$ pip install --upgrade pip
$ pip install dbt-bigquery
Check the version of dbt.
$ dbt --version
Core:
- installed: 1.3.1
- latest: 1.3.1 - Up to date!
Plugins:
- bigquery: 1.3.0 - Up to date!
Create a project named jaffle_shop. We will be asked questions interactively.
$ dbt init jaffle_shop
04:58:32 Running with dbt=1.3.1
Which database would you like to use?
[1] bigquery
(Don't see the one you want? https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/available-adapters)
Enter a number: 1
[1] oauth
[2] service_account
Desired authentication method option (enter a number): 2
keyfile (/path/to/bigquery/keyfile.json): </PATH/TO/YOUR CLIENT SECRET FILE> (e.g., /Users/BBaggins/.dbt/dbt-tutorial-project-331118.json)
project (GCP project id): <PROJECT ID>
dataset (the name of your dbt dataset): jaffle_shop
threads (1 or more): 1
job_execution_timeout_seconds [300]: 300
[1] US
[2] EU
Desired location option (enter a number): 1
04:59:32 Profile jaffle_shop written to /Users/xxx/.dbt/profiles.yml using target's profile_template.yml and your supplied values. Run 'dbt debug' to validate the connection.
04:59:32
Your new dbt project "jaffle_shop" was created!
For more information on how to configure the profiles.yml file,
please consult the dbt documentation here:
https://docs.getdbt.com/docs/configure-your-profile
One more thing:
Need help? Don't hesitate to reach out to us via GitHub issues or on Slack:
https://community.getdbt.com/
Happy modeling!
The project was created as follows.
.
├── jaffle_shop
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── analyses
│ ├── dbt_project.yml
│ ├── macros
│ ├── models
│ │ └── example
│ │ ├── my_first_dbt_model.sql
│ │ ├── my_second_dbt_model.sql
│ │ └── schema.yml
│ ├── seeds
│ ├── snapshots
│ └── tests
└── logs
└── dbt.log
Also, a yaml file has been created in ~/.dbt/profiles.yml.
$ cat ~/.dbt/profiles.yml
jaffle_shop:
outputs:
dev:
dataset: jaffle_shop
job_execution_timeout_seconds: 300
job_retries: 1
keyfile: <PATH TO CLIENT SECRET FILE>
location: US
method: service-account
priority: interactive
project: <PROJECT ID>
threads: 1
type: bigquery
target: dev
You can check the connection to BigQuery with the following command.
$ dbt debug
Connection test: [OK connection ok]
Modeling
Let us create a file named customers.sql in the models directory. Then put the following SQL in the customers.sql file.
with customers as (
select
id as customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
from jaffle_shop.raw_customers
),
orders as (
select
id as order_id,
user_id as customer_id,
order_date,
status
from jaffle_shop.raw_orders
),
customer_orders as (
select
customer_id,
min(order_date) as first_order_date,
max(order_date) as most_recent_order_date,
count(order_id) as number_of_orders
from orders
group by 1
),
final as (
select
customers.customer_id,
customers.first_name,
customers.last_name,
customer_orders.first_order_date,
customer_orders.most_recent_order_date,
coalesce(customer_orders.number_of_orders, 0) as number_of_orders
from customers
left join customer_orders using (customer_id)
)
select * from final
Delete the /models/example folder and edit models in dbt_project.yml as follows.
models:
+ jaffle_shop:
+ +materialized: table
- example:
- +materialized: view
models:
jaffle_shop:
+materialized: table
The directory will look like this.
.
├── jaffle_shop
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── analyses
│ ├── dbt_project.yml
│ ├── macros
│ ├── models
│ │ └── customers.sql
│ ├── seeds
│ ├── snapshots
│ └── tests
└── logs
└── dbt.log
dbt run command create tables in BigQuery from .sql files under the /models directory.
$ dbt run
This will create a customers table in the BigQuery dataset jaffle_shop.
References