What is Product Lifecycle
The product lifecycle is a framework that illustrates the progression of a product through various stages from its conceptualization to its withdrawal from the market. This lifecycle is traditionally divided into four main stages: Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline. Each stage is characterized by different market dynamics, challenges, and opportunities. Understanding the product lifecycle is vital for businesses as it helps in making strategic decisions regarding product development, marketing, pricing, and resource allocation.
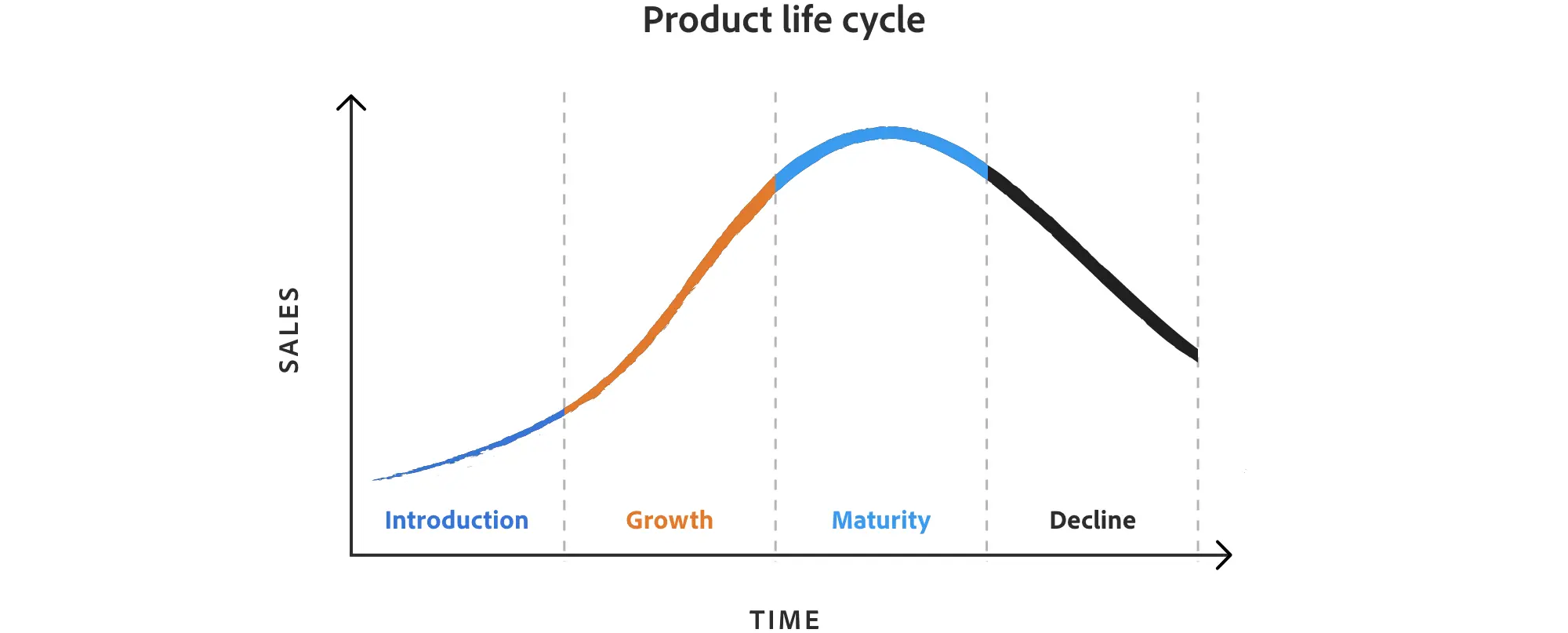
Product life cycle stages and how to use them
The importance of the product lifecycle cannot be overstated. It serves as a roadmap for managing a product efficiently throughout its existence. By recognizing the stage in which a product is, businesses can anticipate market changes and customer demands. Moreover, it guides companies in identifying the right time to invest in innovation or discontinue a product, thus helping in resource optimization and risk minimization.
Phases of the Product Lifecycle
Introduction Phase
-
Market Research
Before a product is introduced to the market, extensive research is conducted to identify the potential customer base, their needs, and preferences. Market research helps in understanding the existing competition, estimating demand, and identifying potential gaps that the new product can fill. It involves collecting data from various sources, analyzing trends, and gathering customer feedback. -
Product Development
Once the market research is complete, and a need or opportunity is identified, the product development process begins. At this stage, ideas are turned into tangible products. This involves design, prototyping, testing, and finalizing the features and specifications of the product. It’s crucial that product development is aligned with the needs and expectations identified during the market research to ensure that it satisfies customer demands. -
Launch Strategies
After the product has been developed, it's time to introduce it to the market. The success of this stage often hinges on the effectiveness of the launch strategy. This strategy should include identifying the target audience, setting the right price, and planning promotional activities. It is also crucial to ensure distribution channels are in place so that the product is available to consumers. Often, companies will use a mix of traditional marketing and digital marketing techniques to create awareness about the new product.
Growth Phase
-
Increasing Market Share
During the growth phase, the product starts gaining acceptance, and sales begin to increase. One of the primary objectives during this phase is to increase market share. This can be achieved through various strategies such as improving product features, entering new markets, or implementing aggressive marketing campaigns. -
Scale and Expansion
As the product gains traction, it's essential to scale operations to meet the increasing demand. This could involve expanding production capacity, broadening distribution networks, or entering new geographic locations. The ability to efficiently scale is critical in sustaining the growth momentum. -
Enhancements and Differentiation
During the growth phase, competitors might enter the market with similar products. To maintain an edge, companies often look to enhance their products by adding new features or improving existing ones. Creating differentiation through unique selling propositions is also crucial in establishing the product as a market leader.
Maturity Phase
-
Market Saturation
At the maturity stage, the market becomes saturated, and sales growth slows down. The product has reached its peak market share, and competition is often intense. At this point, companies must focus on maintaining their market position. -
Competition and Pricing Strategies
During the maturity phase, managing competition becomes critical. Companies might have to consider revising their pricing strategies to remain competitive. Promotional activities, discounts, and customer loyalty programs can also play a significant role in retaining market share. -
Brand Loyalty and Customer Retention
At this stage, building and maintaining brand loyalty is essential. Companies need to focus on customer retention strategies, such as excellent customer service, rewards programs, and regular engagement through various channels.
Decline Phase
-
Market Contraction
The decline phase is characterized by a decrease in sales and market share. This could be due to various factors such as technological advancements, changing customer preferences, or increased competition. The market contracts, and profitability diminishes. -
Harvesting and Divestment
Companies need to make strategic decisions during the decline phase. Some might opt for harvesting, which involves reducing investments and costs associated with the product to extract maximum profits before eventually phasing it out. Another option is divestment, where companies might sell off the product line or business segment associated with the declining product. -
Product Discontinuation
Ultimately, if the product is no longer viable or if it doesn't align with the company's long-term strategy, the product may be discontinued. This means that the company stops the production and sales of the product. It is essential for this process to be managed carefully to minimize any negative impact on the company's brand and to effectively communicate the change to customers and stakeholders.
In some cases, companies may choose to reinvent or rebrand the product instead of discontinuing it. This can sometimes breathe new life into a product that is in the decline phase.